There have been discussions about internal links in the app world recently. Although they have been present in app environments for a long time, it is important to grasp how they function in apps. If you want to know more, keep reading!
Despite being around for some time in the app world, internal links have been the subject of much discussion in recent months.
Deep linking is a technique for improving user experience and boosting conversions and revenues. You might have heard the term before, and you might have been looking for a quick, non-technical explanation of the basics.
What are deep linking?
Are deep links supported in Android and iOS apps?
You’ll see the item from your browser, in the mobile version of the web, when you share this URL with someone -a family member, friend, acquaintance, etc. This occurs even if the user has downloaded the app to his device. When creating deep links from a website, they are not compatible with native mobile apps. The user must open his app and look for the product in it, a waterproof sports camera in this instance. It can be difficult to find items on Amazon’s massive site.
A deep link is a linteligent ink that takes you to a specific content within the app if you have installed or website.
How should we react to it?
Instead of going to the app’s homepage, deep links point directly to the app’s content. With this approach, if we want to share a product with the app, the link will open the product content, not the app’s homepage.
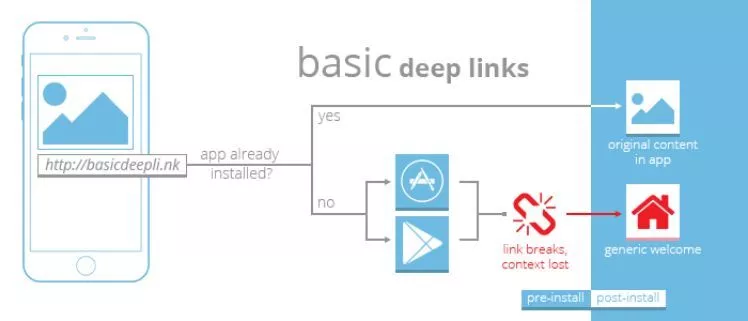
1. Basic Deep link
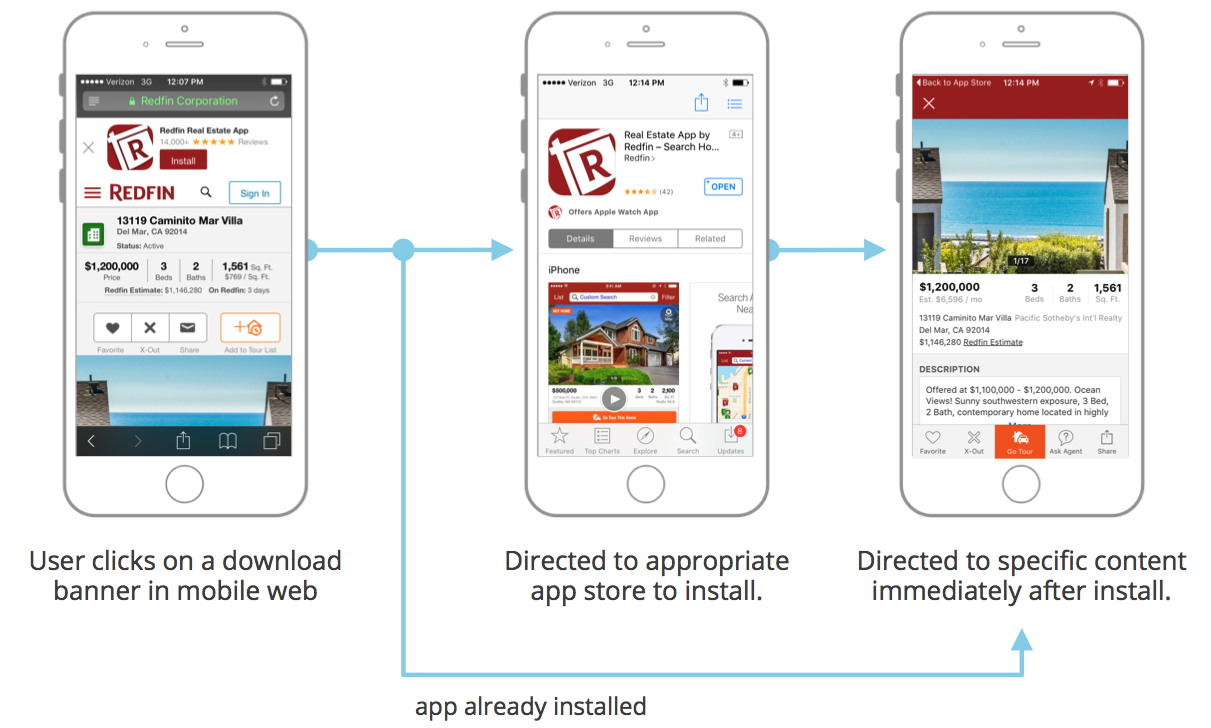
2. Deferred Deep Links
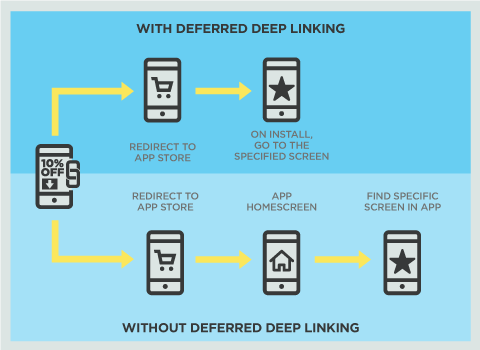
3. Contextual Deep Links
Mobile App Deep linking give users what they want, when they want it
Android and Apple supports deep linking.
Google App Links is Android’s version of iOS universal links.
In iOS, you can use deep links to link to specific content.
With the release of iOS 9.0, Apple introduced universal links. This solution sought to address the problem of deep link functionality in apps by utilising URI schemes.
When you open an iOS link, look for the app if you have it installed. If it’s not installed, the content will open through Safari. A universal link is a standard web link that links to both the web and the content of a web app.
Additionally, according to a Branch.io study, universal links can boost conversion by as much as 40%.
In fact, they operate in much the same way: They are regular web links that connect to a website and content within the app. It leads to a better user experience, but uptake has been sluggish because not all Android versions support it.
Facebook offers Deep Linking functionality.
In 2014, Facebook developed the App Links standard to address the issues with deep link URI schemes. There are two components to app links:
It is time to wrap up.
In spite of the fact that deep linking operates similarly on all platforms, each flavour has a technical foundation. However, mobile applications must implement deep linking as part of app design in terms of user experience and usability. However, in order to do this, you must have a developer who understands how deep linking works, since it frequently includes web and mobile optimisation.
It’s currently a necessity for businesses and a great asset for IT professionals to develop Android apps. Looking at the statistics is all one needs to do to …
Is a custom app required for your next project? Do you want to redesign an existing app or create a new one?
It may seem that creating a mobile application is as simple as snapping your fingers, and that we will have our project up and running in no time …
Fintech investment has grown vertiginously in England and worldwide in recent years, reaching a value of 179 million dollars by 2022. The increase … has been driven largely by the rise of investment in companies developing products to address the investment needs of women and other groups trading lesser volumes of cryptocurrency, such as real estate and impact investing.
An app can be a goldmine for a company, serving as a sales boosting tool, a marketing device, or …
Every application has already been developed, but Super Apps are here to make life easier. Super Apps are a new type of app, …
Deep linking for re-engagement and retention is important.
Abandonment rates (email marketing/e-commerce) are rising.
Users can easily decide not to complete their purchase after browsing, shopping, and filling their cart, after browsing, shopping, and filling their cart.
A proactive approach to re-engaging customers who leave their shopping cart full of items is to send them emails.
About 45% of cart abandonment emails are opened, and 21% are clicked. Even more important, contextually relevant emails may recover as much as 1% of potential lost revenue. (Sitecore)
A fashion retailer has set up an automated process that sends emails to customers who leave items in their shopping carts.
The user is taken to the checkout page using a deep linking solution, where the items that were left in the cart are already conveniently populated.
Users (friend referrals/game play) are how new users are acquired.
Whether it’s printed or digital, word-of-mouth remains a powerful method for creating product and brand awareness.
Consumers are four times more likely to purchase when referred by a friend, so it is no surprise that many firms encourage existing customers to invite their friends to join in the fun.
Word-of-mouth has two purposes in the fiercely competitive gaming sector: existing users become more loyal and keep playing, and new app users are referred and join as a result.
A head-to-head game was incentivized for users of a gaming app using a very simple and quick process in this use case.
The friend is magically brought to the app’s waiting area after downloading the game from the App Store and launching the app, by clicking on a WhatsApp link sent by the gamer. Let the games begin.
Average order value on social media and retail (Combined)
AOV is a measure of the average order amount over a specific period of time. This KPIs provides an opportunity for low-hanging fruit. If a shopper is about to make a purchase, why not provide them with suggestions for other products they might want?
Between now and 2024, the percentage of eCommerce revenue on mobile is expected to increase from 64% to 67%, indicating that mobile apps are the best way to increase AOV.
A fashion brand uses Instagram to advertise an “outfit of the day” story, which includes different products (see example below). When shoppers swipe up, they are redirected to an AppsFlyer social landing page (to prevent Instagram from breaking the link).
When shoppers tap on the “check it out now” CTA button, they are taken to a pre-populated check-out page in the app, including all the items that were featured in the story.
SMS banking: Process abandonment (Traditional banking /SMS)
75% of finance sector forms are dropped because customers find them too difficult to complete. Digital journeys are particularly susceptible to dropoff rates when it comes to insurance.
What if finserv companies could assist their customers by allowing them to take advantage of CX-superior apps?
Companies that are ahead of the curve are already doing this.
Using one or more of their owned media channels in combination with deep linking to remind customers of the form they left behind and bring them directly to the drop-off point, they can easily complete their desired action with minimal hassle involved.
A form-abandoning customer can be engaged using a deep linking product that dynamically creates a unique and personalized URL for each of them in the example provided.
An SMS messaging platform receives the link and schedules a reminder SMS containing a CTA to finish filling out the form. When the link is clicked, the app opens in the correct location so that clients can continue where they left off.
Build apps that continuously and intimately connect with customers—and you will accomplish two key objectives at once. You can rescue form submissions from customers who are highly engaged while simultaneously satisfying customers by helping them achieve their original goals.
Implementing deep linking is crucial.
It’s relatively simple to create deep links with SAAS products from deep linking providers. A handful of them provide SAAS products for creating deep links for mobile marketing campaigns.
Marketers and product managers use deep linking solutions to define the journeys they want their end-users to take once they click on the deep links they create:
It’s also possible for marketers and product managers to gain a better understanding of campaign performance by measuring installs, revenues, paying user share, and LTV, or by capturing the sources of users who have clicked on deep links.
Are developers involved in deep linking implementations? In most cases, developers are involved, since the app must open on the deep-linked page. A good deep linking solution provides adequate hand-offs between developers and marketers/product managers.
It is my final contention about implementing deep linking. You should choose a provider that offers much more than just that. Using another mobile marketing technology stack is usually less desirable than employing a sophisticated mobile marketing platform that includes deep linking capabilities as a core feature.
How to create a deep link
Implementation of deep links for Android
As an example of using deep links for Android, suppose your deep link URL is yourapp://path/ and your app’s package ID is com.yourapp.example.
Solución de JavaScript
An old and common technique to solve this problem is to use iframe to load the deep link URL, and have a delayed JavaScript code to redirect to the store:
When you do this, the browser tries to load yourapp://path/ first.
If your app is installed, it opens, and the following JavaScript does not run.
If your app is not installed, nothing happens when you load yourapp://path/. After 2 seconds, the JavaScript code redirects the user to the Play Store, where they can install the app.
However, there is a small problem with this code: after the app is opened and the user returns to their browser, the JavaScript code may redirect them back to the Play Store. Therefore, we can optimize the process by reviewing the time the user returns to their browser to determine if they need to be redirected to the store or not:
Solución de intent
Since the release of Chrome for Android version 25 or later, the above code has stopped working, as mentioned in the Chrome documentation. Fortunately, Google offers a better solution using the intent URL. When a user clicks the URL intent://path/#Intent;scheme=yourapp;package=com.yourapp.example;end, the following happens:
- if the app is installed, Chrome opens the app.
- if the app isn’t installed, Chrome opens the Play Store.
¿Cuál solución de deep links debo utilizar en King of App?
JavaScript solution
Similar to Android, there is also a JavaScript trick for iOS:
html <script>
window.location.replace(“yourapp://path/”); setTimeout(function () {
window.location.replace(“https://itunes.apple.com/app/id12345678”); }, 2000);
</script>.
- if the app is installed, the first relocation code opens the app and the next script is not executed.
- if the app is not installed, the first relocation code does nothing and the idle timeout feature redirects the user to the App Store.
Solución de links universales
Starting with iOS 9, Apple introduced the universal link, which works similarly to Android’s intent, but requires more configuration. And, starting with iOS 9.2, the JavaScript fix stopped working because Apple introduced a modeless prompt window.
In order to enable universal links, you must have an SSL-certified domain (for example, https://yourdomain.com/) associated with your app and display a special JSON file at https://yourdomain.com/apple-app- site-association similar to the following:
This file tells your device which route works as the deep link for each app.
Then you need to add applinks:yourdomain.com to your com.apple.developer.associated-domains mapping inside XCode:
You can associate a domain with several applications or vice versa.
You must then adopt the UIApplicationDelegate methods for delivery (specifically, application:continueUserActivity:restorationHandler:) so that your application can receive a link and handle it appropriately.
Suppose you associate https://yourdomain.com/dress/ with your application by setting “paths”:[ “/dress/”] in the JSON file. When the user clicks the link https://yourdomain.com/dress/1 in Safari, the following happens:
- if the app is installed, the app is opened, and https://yourdomain.com/dress/1 is sent to the UIApplicationDelegate. There you can use it to decide which view you want to open.
- if the app is not installed, https://yourdomain.com/dress/1 opens with Safari, and you can continue to display the product on your website or redirect the user to the App Store.
Universal Links seems to be a perfect solution for iOS. Unfortunately, however, they also have their limitations.
- Universal links only work with Safari and Chrome.
- When another website redirects with a universal link, it only works if the click takes place within Safari or Chrome. For example, if in your email application there is a link https://anotherDomain.com/ that redirects to the universal link https://yourDomain.com/dress/1, this does not work as a deep link to your application. However, if the user clicks the link https://anotherDomain.com from Safari, this does work.
- Universal links do not work if you paste the link directly into the address bar.
- Universal links do not work if the redirect is triggered by a JavaScript code.
- Universal links do not work when you open the link programmatically within your application (eg with openUrl).
First, in the builder, you have to go to services, and click in the marketplace. Select the deep linking service and add it.

Once added you will see these options.
You will find the most common deeplinks already preconfigured in the service: WhatsApp, Facebook, Twitter, Telegram, Instagram, Linkedin and Snapchat.
Just open clicking to activate the option.
Otherwise you will have to configure the custom service by adding the custom deep link.
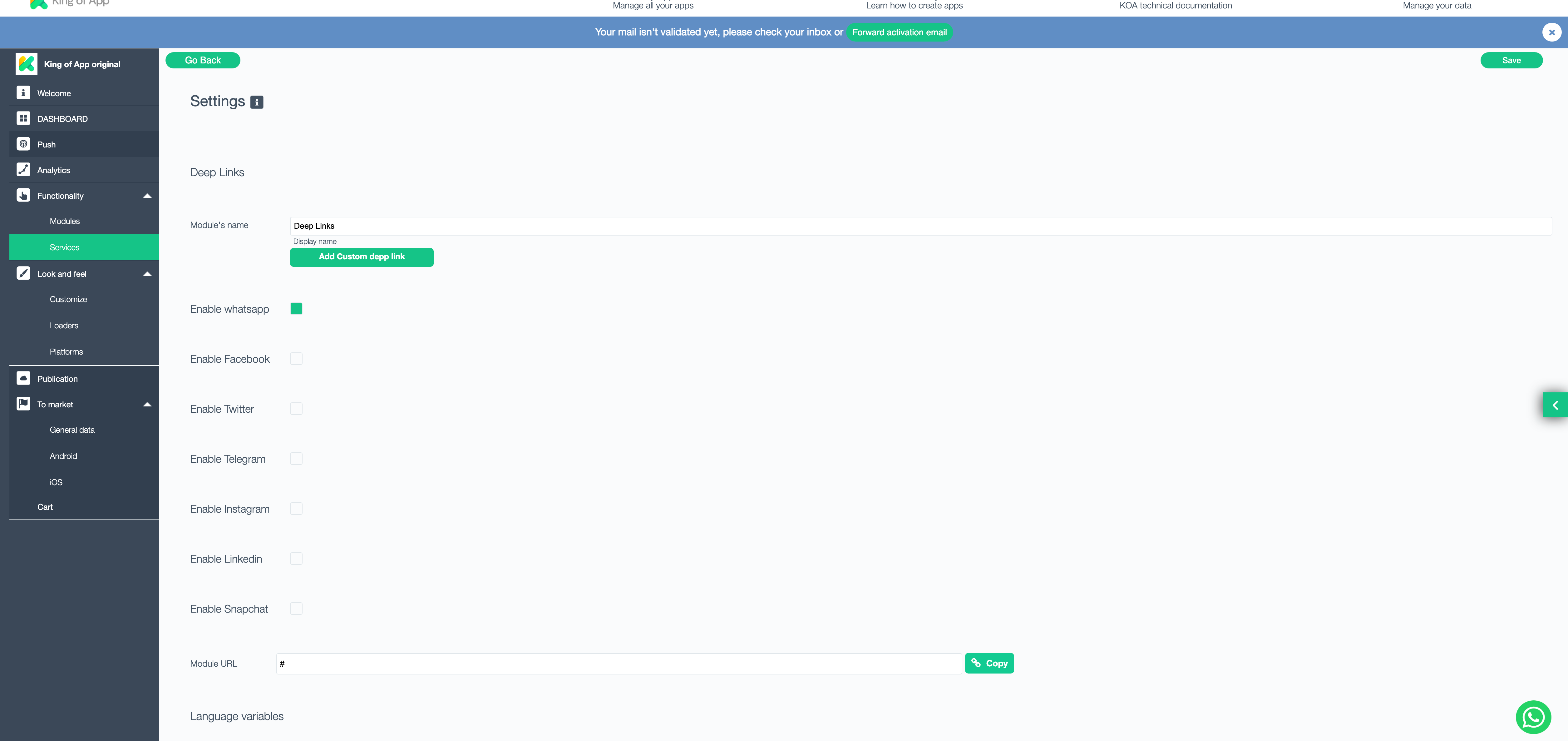
How to configure a custom a deep link
There is no magic formula from this point, for this reason during the article we have been explaining step by step how this type of link works.
It is best to look for the documentation of each app / platform how to build the link. example: https://faq.whatsapp.com/425247423114725/?cms_platform=iphone
There will be cases where the deep link of ios and android are different, therefore we advise you to use an intelligent url shortener, such as the one you can find on our website in the resources section or also within our wordpress mobile suite, you have a intelligent one link creator.